REGULATED POWER SUPPLY
it is the terminal voltage that will remains almost constant regardless of the amount of current drawn from it.
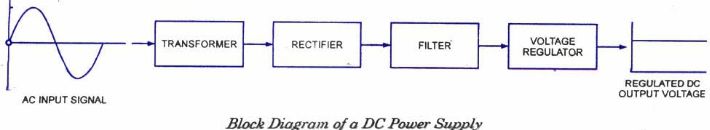
- TRANSFORMER: its job is either to step up or step down the a.c supply voltage to suit the requirements of the solid states electronics devices and circuit fed by the D.C power supply. It also provides isolation from the supply line.
- RECTIFIER: It is a circuit which employs one or more diodes to convert a.c voltage into pulsating d.c voltage.
- FILTER: The function of this circuit element is to remove the fluctuation or pulsations (called ripples) present into the output voltage supplied by the rectifier.
- VOLTAGE REGULATOR: It main function is to keep the terminal voltage of the d.c supply constant even when (a) a.c input voltage to the transformer varies or (b) the load varies.
Using zener diode and transistor are used for voltage regulation purposes. It’s impossible to get 100% constant voltage but minor variations are acceptable for most of the jobs
